OV329 and GABA-aminotransferase inhibition
OV329 Posters and Publications »
overview
OV329 is a next-generation GABA-aminotransferase (GABA-AT) inhibitor being developed as a potential medicine for rare and treatment-resistant forms of epilepsy and seizures. Ovid believes OV329 is significantly more potent than prior GABA-AT inhibitors which may confer seizure reduction efficacy, enhanced safety, and lower dosing.
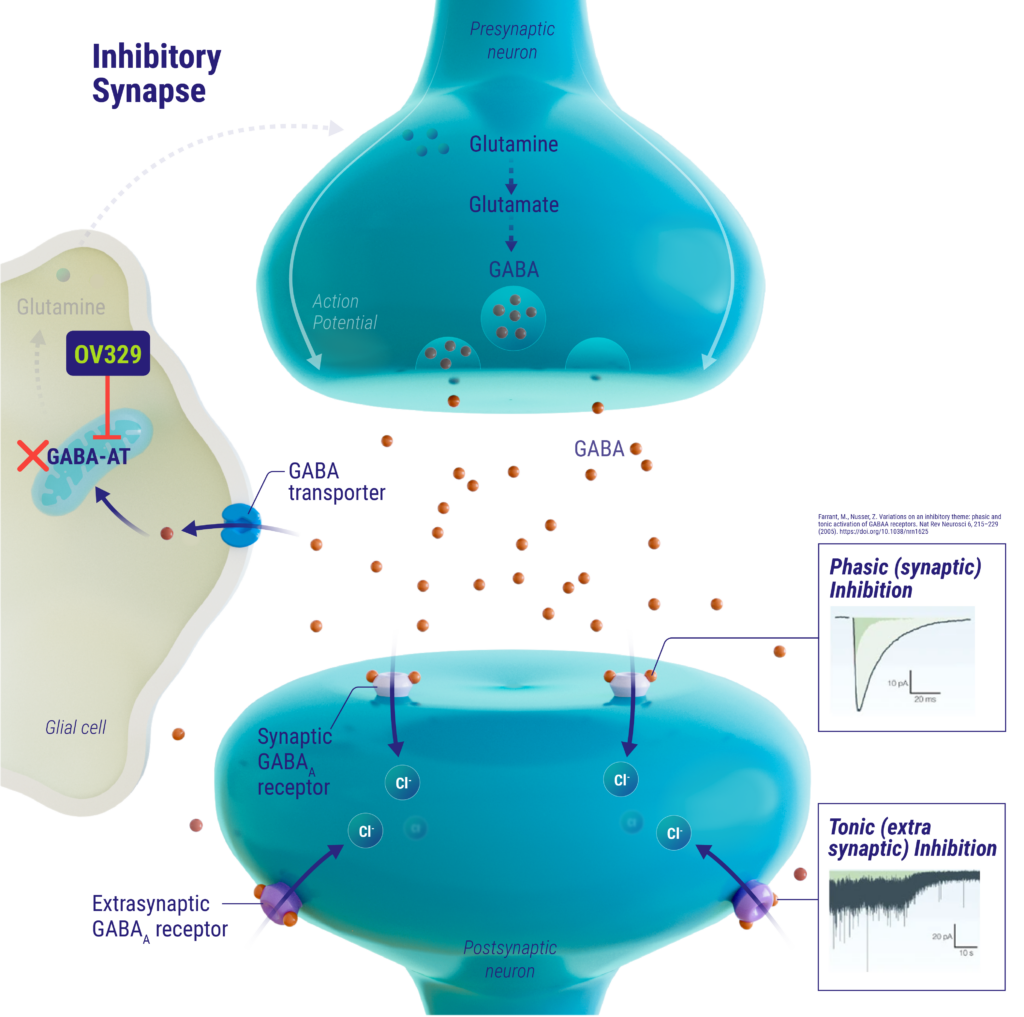
mechanism of action
γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and is primarily catabolized by the enzyme GABA aminotransferase (GABA-AT). Low levels of GABA in the brain have been linked to neuronal hyperexcitability, which can lead to seizures. OV329 inhibits GABA-AT activity, thereby increasing GABA levels in the brain, resulting in suppression of neuronal hyperexcitability associated with seizures. OV329 may be a best-in-class GABA-AT inhibitor that could offer enhanced efficacy with an improved benefit-risk profile.
development
OV329 is currently in a Phase 1 study with healthy volunteers to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetic profile and target engagement associated with single and repeated oral doses of OV329. The Phase 1 study will measure two potential biomarkers for target engagement via magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Ovid expects to have topline data from this ongoing Phase 1 study in 2025.
Prior evaluation of OV329 in preclinical seizure and epilepsy models indicate that OV329 significantly reduced focal and generalized seizures, including pharmaco-resistant seizure phenotypes. Improvement in seizure outcomes could be achieved with repeated, low dosing which have correlated with increases in brain GABA levels and tonic inhibitory neuronal signaling. Additionally, pre-clinical models have shown that OV329 does not preferentially accumulate in retina, eye, and brain tissues. This study may suggest that OV329’s short half-life, quick tissue elimination properties, and prolonged pharmacodynamic effect may reduce the risk of ocular accumulation occurring.
For additional information on OV329 non-clinical data, please click here.