OV350 & KCC2 Library
Ovid hosted a KCC2 Download Day in November 2024. For information about the session, please click here.
OV350 and KCC2 Posters and Presentation »
overview
Ovid’s K+Cl– cotransporter 2 (KCC2) program is a portfolio of potential first-in-class direct activators of the KCC2 transporter. These activators may have broad therapeutic opportunities across a range of CNS conditions. Ovid exclusively in-licensed the KCC2 portfolio from AstraZeneca in 2022.
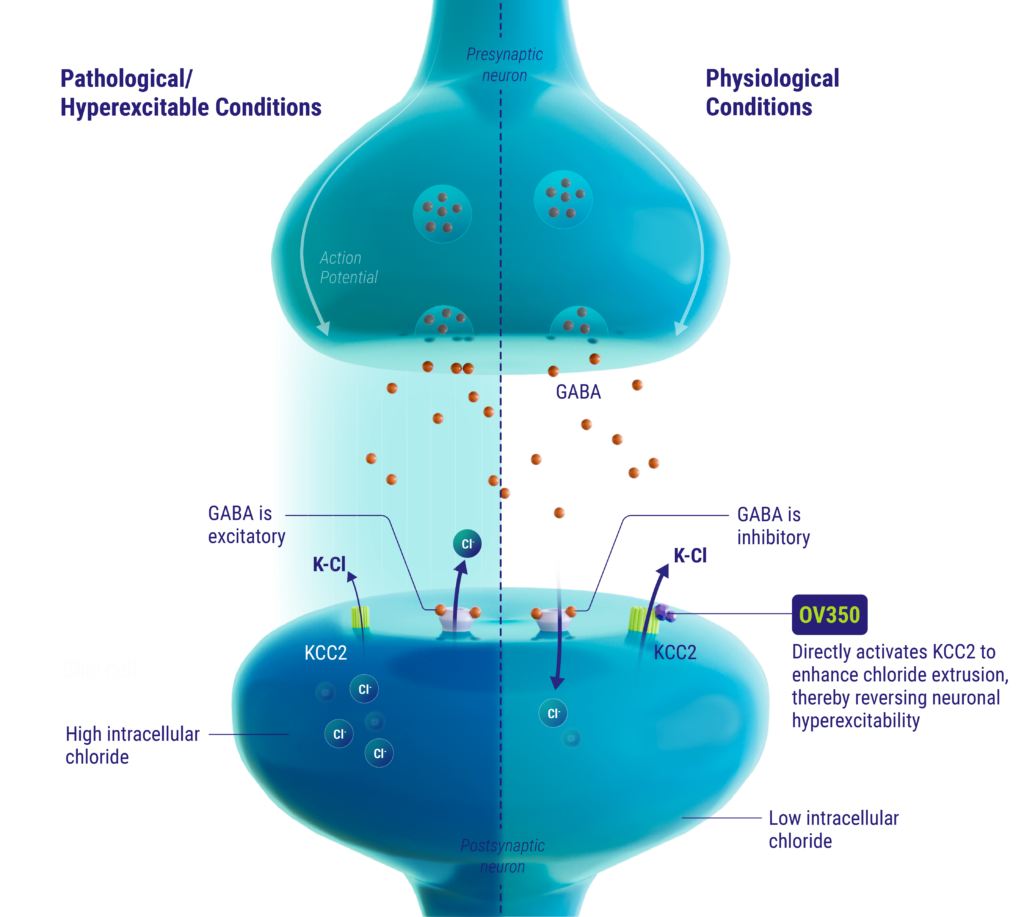
mechanism of action
The KCC2 transporter is a neuron-specific chloride extruder that is critical for maintaining GABA’s inhibitory function in the mature brain. Directly activating KCC2 can restore neuronal inhibitory and excitatory balance to bring a hyperexcited neuron back into homeostasis. OV350 directly activates KCC2, thereby restoring chloride homeostasis in neurons and subsequently reducing hyperexcitability.
development
In vivo proof-of-concept studies in animals have established that restoring KCC2 activity leads to reduced seizure sensitivity and seizure-induced mortality. In one preclinical model, designed to mimic the acute seizure state of status epilepticus (SE), OV350 in combination with diazepam terminated seizures, restored the efficacy of diazepam, and reduced the amount of associated neuronal loss following injury. Preclinical mechanistic studies have also demonstrated that OV350 was well-tolerated and did not induce sedation.
In 2022, Ovid evaluated several compounds in the KCC2 portfolio and began optimizing the lead candidate, OV350, for multiple possible formulations. Dual formulations are optimal for patients who are treated acutely in the hospital and need to maintain seizure reduction in an out-patient setting.
Ovid initiated the OV350 phase 1 study in Q1 2025. For additional information on OV350 non-clinical data, please click here.
potential indications
Ovid is also progressing its KCC2 library, which comprises multiple compounds with different pharmacology and combinations of effects across neurological conditions with high unmet need including: neuropsychiatric, neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative application.